New Release: Continuous Machine Learning (CML) is CI/CD for ML
Today we're launching Continuous Machine Learning (CML), a new open-source project for CI/CD with ML. Use it to automate parts of your ML workflow, including model training and evaluation, comparing ML experiments across your project history, and monitoring changing datasets. Let's bring the power of DevOps to ML or MLOps.

CML release
CI/CD for machine learning
Today, the DVC team is releasing a new open-source project called Continuous Machine Learning, or CML (https://cml.dev) to mainstream the best engineering practices of CI/CD to AI and ML teams. CML helps to organize MLOps infrastructure on top of the traditional software engineering stack instead of creating separate AI platforms.
Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) is a widely-used software engineering practice. It's a validated approach to increasing the agility of software development without sacrificing stability. But why haven't CI/CD practices taken root in machine learning and data science so far?
We see three substantial technical barriers to using standard CI systems with machine learning projects:
- Data dependencies. In ML, data plays a similar role as code: ML results critically depend on datasets, and changes in data need to trigger feedback just like changes in source code. Furthermore, multi-GB datasets are challenging to manage with Git-centric CI systems.
- Metrics-driven. The traditional software engineering idea of pass/fail
tests does not apply in ML. As an example,
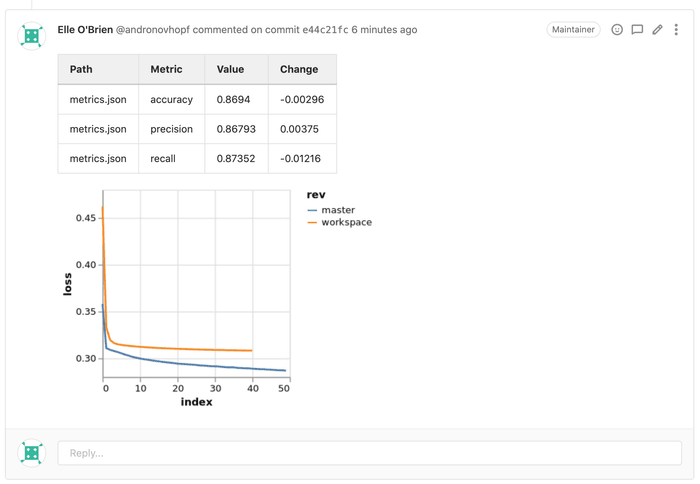
+0.72% accuracyand-0.35% precisiondoes not answer the question if the ML model is good or not. Detailed reports with metrics and plots are needed to make a good/bad model discussion - CPU/GPU resources. ML training often requires more resources to train then is typical to have in CI/CD runners. CI/CD must be connected with cloud computing instances or Kubernetes clusters for ML training.
CI/CD for ML is the next step for the DVC team
Since the beginning, our motivation has been helping ML teams benefit from DevOps. We started DVC because we knew that data management would be a crucial bottleneck, and sure enough, DVC was a big step towards making pipelines and experiments manageable and reproducible. But conversations with our community have brought us to one conclusion again and again: CI/CD for ML is the holy grail.
Over the last 3 years, we've reached some big milestones:
-
We built DVC to address the ML data management problem. Recently, we released DVC 1.0, marking a new and more stable era for our API.
-
DVC has become a core part of many ML team's daily operations. The latest ThoughtWorks Technology Radar says:
"… it [DVC] has become a favorite tool for managing experiments in machine learning (ML) projects. Since it's based on Git, DVC is a familiar environment for software developers to bring their engineering practices to ML practice."
-
An extraordinary team and community have emerged around DVC:
- 15 employees in our organization https://iterative.ai
- 100+ open-source contributors to DVC https://github.com/iterative/dvc and another 100+ open-source contributors to docs https://github.com/iterative/dvc.org
- 2000+ community members in our Discord https://dvc.org/chat and GitHub issue tracker https://github.com/iterative/dvc
- 4000+ regular users of DVC
Now that DVC is maturing, we're ready to take the next step: we want to revolutionize the ML development processes. We want ML experiments to have greater visibility to teammates, shorter feedback loops, and more reproducibility. We want teams to spend less time managing their computing resources and experiments, and more time building value. The goal is to extend the amazing results of DevOps from software development to ML and MLOps.
Continuous Machine Learning release
Today, we're releasing an open-source project https://cml.dev to close the gap between machine learning and software development practices.
CML is a library of functions used inside CI/CD runners to make ML compatible with GitHub Actions and GitLab CI. We've created functions to:
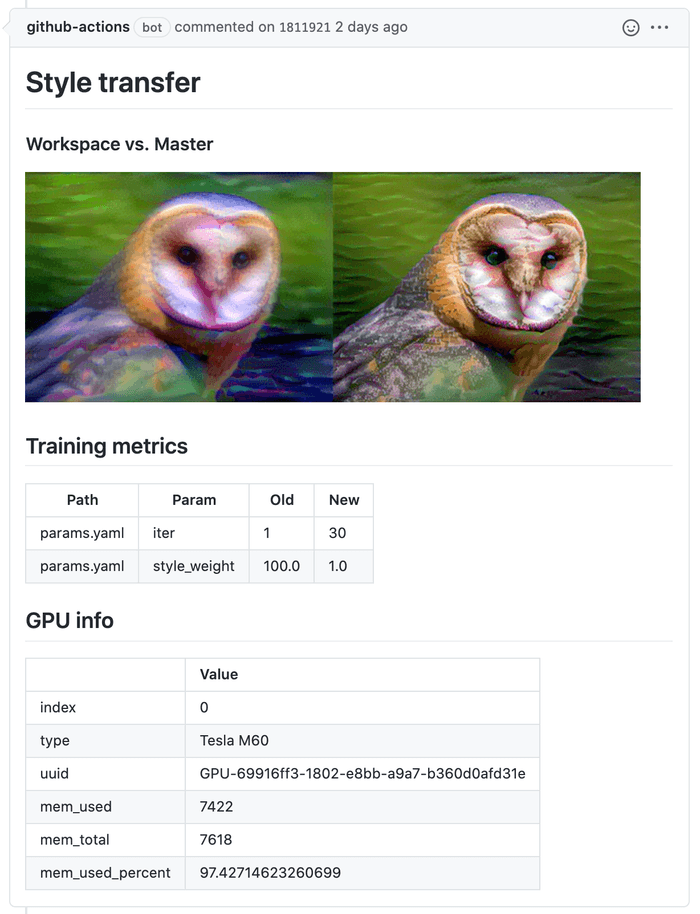
- Generate informative reports on every Pull/Merge Request with metrics, plots, and hyperparameters changes.
- Provision GPU\CPU resources from cloud service providers (AWS, GCP, Azure, Ali) and deploy CI runners using Docker Machine.
- Bring datasets from cloud storage to runners (using DVC) for model training, as well as save the resulting model in cloud storage.
The workflow and visual reports are customizable by modifying the CI
configuration file in your GitHub ./github/workflows/*.yaml or GitLab
.gitlab-ci.yml project. Use CML functions in conjunction with your own ML
model training and testing scripts to create your own automated workflow and
reporting system.
# GitLab workflow in '.gitlab-ci.yml' file
stages:
- cml_run
cml:
stage: cml_run
image: iterativeai/cml:0-dvc2-base1
script:
- dvc pull data --run-cache
- pip install -r requirements.txt
- dvc repro
# Compare metrics to master
- git fetch --prune
- dvc metrics diff --show-md master >> report.md
# Visualize loss function diff
- dvc plots diff --target loss.csv --show-vega master > vega.json
- vl2png vega.json > plot.png
- cml publish --md plot.png >> report.md
- dvc push data --run-cache
- cml send-comment report.mdIn this example all the CML functions are defined in the docker images that
is used in the workflow - iterativeai/cml:0-dvc2-base1. Users can specify any
docker image. The only restriction is that the CML library need to be installed
to enable all the CML commands for the reporting and graphs:
npm i @dvcorg/cmlExamples of docker images can be found in docker directory of the CML the
repository: CML repository.
As you can see, CML is based on the assumption that MLOps can work with traditional engineering tools. It shouldn't require an entirely separate platform. We're excited about a world where DevOps practitioners can work fluently on both software and ML aspects of a project.
The relationship between CML and DVC
CML and DVC are related projects under the umbrella of the same team, but will have separate websites and independent development. The CML project is hosted on a new web site: https://cml.dev. The source code and issue tracker is on GitHub: https://github.com/iterative/cml
For support and communications, the DVC Discord server is still the place to go:
https://dvc.org/chat We've made a new #cml channel there to discuss CML, CI/CD
for ML and other MLOps related questions.
Conclusion
With the rise of AI/ML teams and ML platforms in addition to the software engineering stack, we believe that the industry needs a single technology stack to work with software as well as AI projects. A simple layer of a tool is required to close the gap between AI projects and software projects to fit them into the existing stack and CML is the way to make it.
Our philosophy is that ML projects, and MLOps practices, should be built on top of traditional engineering tools and not as a separate stack. A simple layer of tools will be required to close the gap, and CML is part of this ecosystem. We think this is the future of MLOps.
As always, thanks for reading and for being part of the DVC community. We'd love to hear what you think about CML. Please be in touch on Twitter and Discord!